What Color Is Pluto Planet?
As you gaze up at the night sky, the distant glow of stars twinkling like diamonds, your mind begins to wander to the wonders of the universe.
Among the celestial bodies that captivate our imagination, Pluto stands out as a symbol of mystery and intrigue. But have you ever wondered, what color is Pluto?
It is a question that has puzzled astronomers and space enthusiasts alike for decades. And as we embark on this exploration, we will delve into the fascinating journey of uncovering the true colors of this enigmatic planet, leaving you with a newfound appreciation for the vastness of our universe.
Key Takeaways
- Pluto’s color is predominantly reddish-brown, influenced by chemical compounds like tholins and hydrocarbons.
- The presence of methane on the surface gives Pluto a reddish hue, as methane absorbs blue and green light, reflecting longer wavelengths corresponding to red light.
- The composition of Pluto’s atmosphere and surface, including nitrogen and other gases, can scatter sunlight and contribute to its range of colors.
- Sunlight interacting with Pluto’s surface and atmosphere forms colored molecules, such as tholins, which add to Pluto’s unique color palette.
Pluto’s Color: An Introduction
Pluto’s color, though often debated, remains a fascinating subject within the scientific community. As an audience that desires belonging, it’s important to understand the significance of Pluto’s color.
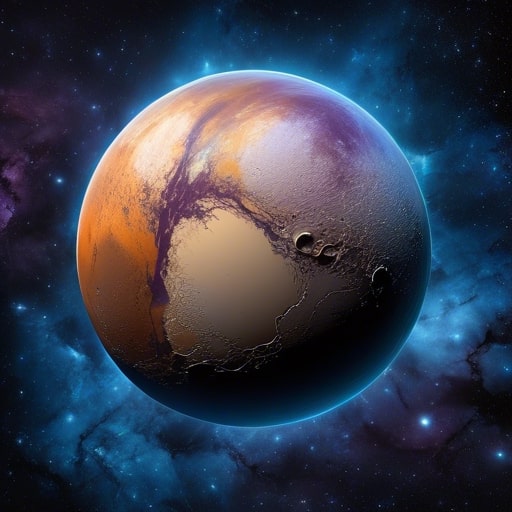
Through extensive observations and analysis, scientists have determined that Pluto’s color is predominantly reddish-brown. This distinctive hue is believed to be a result of various chemical compounds present on its surface, such as tholins and hydrocarbons.
These compounds are formed when ultraviolet light from the Sun interacts with methane and nitrogen in Pluto’s atmosphere.
The reddish-brown color is also influenced by the presence of other organic molecules, which further contribute to the complex and intriguing coloration.
By studying Pluto’s color, scientists gain valuable insights into its composition and the processes occurring on its surface, fostering a sense of belonging within the scientific community.
Early Observations and Assumptions
As you explore the early observations and assumptions surrounding Pluto’s color, it is crucial to consider the initial findings that shaped our understanding of this enigmatic celestial body.
In the early 20th century, astronomers began studying Pluto, hoping to uncover its true color. Initial observations were limited due to technological constraints and the vast distance of Pluto from Earth.
However, through spectroscopic analysis and telescopic observations, scientists made some assumptions about its color. It was believed that Pluto had a reddish hue, similar to Mars, due to the presence of tholins, complex organic molecules formed by the interaction of sunlight and Pluto’s atmosphere.
This assumption was supported by later spacecraft missions, such as the New Horizons mission, which confirmed Pluto’s reddish-brown color.
However, further studies are still needed to fully understand the complex nature of Pluto’s color.
| Early Observations and Assumptions | Findings |
|---|---|
| Limited observations | Reddish hue |
| Spectroscopic analysis | Presence of tholins |
| Telescopic observations | Similar to Mars |
| New Horizons mission | Reddish-brown color |
The Discovery of Pluto’s True Color
Scientists have made significant advancements in uncovering the true color of Pluto through careful analysis and observations.
By studying the light reflected off Pluto’s surface, scientists have determined that its predominant color is a reddish-brown hue, similar to the color of rust.
This discovery was made possible through the use of advanced spectroscopic techniques, which allow scientists to analyze the different wavelengths of light emitted or absorbed by Pluto’s surface.
The reddish-brown color is believed to be caused by complex organic compounds called tholins, which are formed when ultraviolet light from the sun interacts with methane and nitrogen in Pluto’s atmosphere.
These tholins, along with other compounds, settle on the surface and give Pluto its characteristic color.
Understanding the true color of Pluto contributes to our knowledge of its composition and provides valuable insights into the processes occurring on this distant world.
Understanding Pluto’s Atmosphere and Surface
By examining the composition of Pluto’s atmosphere and surface, valuable insights can be gained into the processes occurring on this distant world.
Pluto, despite being classified as a dwarf planet, is a fascinating celestial body that continues to intrigue scientists.
Here are some key points to consider:
Atmosphere:
- Thin and primarily composed of nitrogen, similar to Earth’s atmosphere.
- Contains traces of methane, which gives Pluto its reddish hue.
Surface:
- Covered in a variety of icy compounds, such as nitrogen, methane, and carbon monoxide.
- Features large mountains, flat plains, and icy glaciers.
Studying the atmosphere allows scientists to understand the interaction between gases and sunlight on Pluto.
The composition of the surface sheds light on the geological processes that have shaped this distant world.
Factors Influencing Pluto’s Coloration
Pluto’s coloration is influenced by a combination of factors, including the composition of its atmosphere and surface.
The presence of different chemical compounds on Pluto’s surface plays a crucial role in determining its color.
For instance, the presence of methane on the surface gives Pluto a reddish hue. This is because methane absorbs light in the blue and green regions of the electromagnetic spectrum, reflecting the longer wavelengths that correspond to red light.
Additionally, the composition of Pluto’s atmosphere affects its coloration. The presence of nitrogen and other gases in the atmosphere can scatter sunlight, leading to a bluish appearance.
These factors, along with the interaction between sunlight and Pluto’s surface, contribute to the fascinating range of colors observed on this distant dwarf planet.
The Role of Sunlight in Pluto’s Color
Sunlight plays a crucial role in determining the color of Pluto. The distant dwarf planet’s coloration is influenced by the interaction of sunlight with its surface. Here are two key factors explaining the role of sunlight in Pluto’s color:
- Sunlight and Chemical Reactions: Sunlight triggers chemical reactions on Pluto’s surface, leading to the formation of complex organic compounds. These compounds, known as tholins, are responsible for Pluto’s reddish hue. Sunlight breaks down methane molecules in Pluto’s atmosphere, creating a chain reaction that ultimately produces tholins. The intensity and wavelength of sunlight determine the type and quantity of tholins formed.
- Sunlight and Surface Composition: Sunlight reflects differently off various materials on Pluto’s surface, influencing its color appearance. The composition of Pluto’s surface, which includes nitrogen ice, methane, and other organic compounds, interacts with sunlight in unique ways. These interactions cause the absorption, scattering, and reflection of different wavelengths of light, resulting in the overall coloration of the dwarf planet.
Unraveling the Mystery: The Current Understanding of Pluto’s Color
Understanding the mechanisms behind the coloration of Pluto is essential in unraveling the mystery surrounding its enigmatic appearance. Scientists have made significant progress in deciphering the current understanding of Pluto’s color.
The surface of Pluto exhibits a range of hues, including reddish-brown, yellow, and even patches of white. These colors are believed to be the result of complex chemical processes occurring on its surface.
One theory suggests that a mixture of nitrogen, methane, and other organic compounds interact with solar radiation, leading to the formation of various colored molecules.
Additionally, the presence of tholins, which are organic molecules formed by the interaction of sunlight with gases in Pluto’s atmosphere, contributes to its unique color palette.
Further research and analysis will help deepen our understanding of this intriguing dwarf planet’s colorful nature.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does Pluto’s Color Compare to Other Planets in Our Solar System?
Pluto’s color, when compared to other planets in our solar system, demonstrates unique characteristics. Understanding its composition and surface features allows for a precise scientific analysis, fostering a sense of belonging among those fascinated by celestial bodies.
Can Pluto’s Color Change Over Time?
Yes, Pluto’s color can change over time due to various factors such as seasonal changes in its atmosphere and the presence of different types of ices on its surface.
What Is the Significance of Understanding Pluto’s Color for Future Space Exploration?
Understanding Pluto’s color is significant for future space exploration. By studying its color, scientists can gain insights into its composition, atmosphere, and geological processes. This knowledge can help us better understand the outer reaches of our solar system and potentially find habitable worlds.
Are There Any Theories or Hypotheses About Why Pluto Has Its Specific Color?
There are various theories and hypotheses regarding why Pluto has its specific color. Scientists suggest that it could be due to the presence of compounds like methane and nitrogen on its surface, which interact with sunlight.
How Do Scientists Determine the Exact Color of Pluto?
To determine Pluto’s exact color, scientists analyze the light reflected off its surface. They use spectroscopy, which breaks down the light into different wavelengths, revealing the specific colors present.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Pluto’s true color was discovered to be a reddish-brown hue, contrary to early assumptions. This coloration is influenced by factors such as the presence of nitrogen and methane in its atmosphere, as well as the reflection and absorption of sunlight.
With our current understanding, we continue to unravel the mysteries of Pluto’s color. Its captivating and unique appearance makes it a celestial gem, like a vibrant jewel adorning the vast expanse of our solar system.